As a chemist with extensive experience in organic synthesis, I have witnessed firsthand the critical role of halogenated intermediates in pharmaceutical development. Among these, 2-Bromoindene stands out as a versatile building block, enabling precise functionalization and facilitating complex molecular architectures.
This guide offers an in-depth exploration of 2-Bromoindene’s chemical properties, synthetic applications, practical handling, and sourcing considerations, providing a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners.
Chemical Structure and Properties of 2-Bromoindene
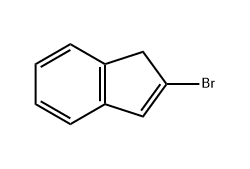
2-Bromoindene is a brominated derivative of indene, with the bromine atom positioned at the 2-carbon of the five-membered ring fused to a benzene ring. Its molecular formula, C₉H₇Br, reflects its potential for halogen-mediated reactivity. The presence of the bromine atom increases the electrophilicity of the adjacent carbon, making it a highly reactive site for cross-coupling reactions. Physicochemically, 2-Bromoindene typically appears as a pale yellow solid with moderate stability under standard laboratory conditions. Its solubility in common organic solvents like dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, and toluene facilitates versatile synthetic applications.
Key Features That Make 2-Bromoindene Useful in Synthesis
Several structural and chemical characteristics underpin the utility of 2-Bromoindene in drug synthesis:
- Halogen Activation: The bromine atom enables efficient participation in palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions, such as Suzuki, Heck, and Sonogashira couplings.
- Aromatic Fused System: The indene framework provides a rigid, planar structure suitable for functionalization without disrupting molecular integrity.
- Selective Reactivity: Its electrophilic site allows targeted transformations, minimizing side reactions in multistep syntheses.
How 2-Bromoindene Serves as a Synthetic Intermediate
In pharmaceutical chemistry, 2-Bromoindene functions as a strategic intermediate for constructing complex molecules. Its halogen atom acts as a synthetic handle, permitting the introduction of diverse substituents through cross-coupling, nucleophilic substitution, or metalation strategies. Many indene-based drugs and natural product analogs rely on 2-Bromoindene as a precursor for the formation of carbon-carbon or carbon-heteroatom bonds. By employing 2-Bromoindene, chemists can efficiently assemble fused ring systems, heterocycles, or extended aromatic frameworks crucial for bioactivity.
Applications in Pharmaceutical Compound Development
The intermediate has been widely utilized in the development of:
- Indene-derived enzyme inhibitors
- Anticancer agents with fused aromatic rings
- Central nervous system modulators leveraging indene scaffolds
Its role is pivotal in diversifying lead compounds while maintaining synthetic efficiency and minimizing step count. Researchers favor 2-Bromoindene for its capacity to enable late-stage functionalization, a valuable asset in iterative drug optimization.
Basic Handling and Safety Considerations
Despite its utility, 2-Bromoindene requires careful handling. Key considerations include:
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves and goggles.
- Working in a well-ventilated fume hood due to potential irritant vapors.
- Avoiding prolonged exposure to heat and light to maintain stability.
Proper storage in airtight containers, under inert atmosphere if needed, to prevent degradation or unwanted side reactions.
Availability and Purity Options for 2-Bromoindene
For laboratory and industrial use, sourcing high-purity 2-Bromoindene is essential. Commercial suppliers typically provide purity ranging from 95% to >99%. Selecting reputable manufacturers ensures minimal contaminants, consistent reactivity, and reproducibility in synthetic campaigns. Bulk availability supports both research-scale reactions and larger pharmaceutical production needs, making it a reliable choice for ongoing drug development projects.
2-Bromoindene represents a cornerstone intermediate in modern pharmaceutical synthesis. Its halogen functionality, structural rigidity, and versatile reactivity enable chemists to construct diverse and complex molecular architectures efficiently. Proper handling, awareness of its chemical properties, and sourcing high-quality material are critical for maximizing its utility. For researchers and practitioners, mastery of 2-Bromoindene chemistry is indispensable in advancing drug discovery and development.



